Monkeypox Virus belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus in the family Poxviridae. The genus Orthopoxvirus also includes variola virus (which causes smallpox), vaccinia virus (used in smallpox vaccine), and cowpox virus. Monkeypox Virus was first discovered in 1958 after two outbreaks of a smallpox-like disease appeared in monkey colonies held for research, hence the name 'monkeypox'.
Monkeypox Virus is a rare disease that belongs to the same family of viruses as smallpox.
Monkeypox Virus infections occur primarily in Central and West African countries and have been rarely seen outside of
Africa. The natural reservoir of the monkey flower is unknown. However, African rodents and non-human primates (such as monkeys) can harbor the virus and infect humans.
What is monkey flower?
It is a rare disease that can begin with flu-like symptoms and swelling of the lymph nodes before progressing to a rash covering the face and body. Although it “typically” causes a milder infection than smallpox, the virus can be spread between humans through direct contact with monkeypox lesions, bodily fluids, and even contaminated materials such as clothing or linens.
It is confirmed that most monkeypox infections can last 2 to 4 weeks. People who have likely been exposed to the virus should be monitored for signs of infection for about 3 weeks after exposure.
While all strains can cause infection, strains circulating in West Africa generally cause less severe disease. The first report of the virus transmitted in another region was made in 2003 after the importation of exotic pets. Before infecting humans, the virus caused infections in non-African captive species, including prairie dogs. This report is the first to be cited outside of Africa.
Human-to-human infection occurs via aerosols, similar to COVID-19. While it can also be spread through large respiratory droplets that usually cannot travel more than 1 to 3 feet, prolonged face-to-face contact is typically required for transmission to occur.
Monkeypox Virus was first identified in 1958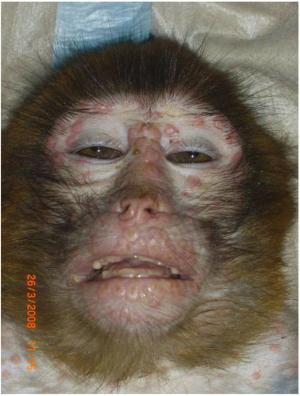
The first discovery of Monkeypox Virus was made in 1958 during a disease outbreak in monkeys kept at an animal facility in Copenhagen, Denmark . Until 1970, no cases of human monkeypox were detected in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. There may be several species harboring the virus, but the only reported case of monkeypox isolated from a wild animal was a diseased squirrel.
The natural reservoir of the monkey flower is currently unknown. But a number of African rodent species are believed to play a role in transmission. Monkeypox Virus is a 'rare but serious' disease.
Since 2017 , 218 cases have been confirmed in Nigeria , and 8 cases have been reported in international travelers from Nigeria, including one case in Texas and the current case in July 2021.
Also, due to the health risks associated with a single case of monkeypox, they should promptly report suspected cases to local public health authorities "regardless of whether they are investigating other potential diagnoses."
Two different species of monkeypox have been described: Congo Basin and West African species. The Congo Basin virus is more virulent and contagious.
Treatment of monkeypox infection
There is currently no standard treatment. For monkeypox, patients are at risk for complications that can include pneumonia, sepsis, and corneal infection leading to blindness. There is a lack of understanding about the most common and most important complications of this disease, including the death toll or post-infection effect rates.
Researchers rely heavily on case series and individual case reports to identify cases.
It is stated that since the monkeypox virus is closely related to the virus responsible for smallpox, the smallpox vaccine can be used to effectively protect people from infection.
What are the symptoms?
Initial symptoms include fever, headache, swellings, back pain, aching muscles, and a general malaise.
Once the fever subsides, a rash may develop that usually starts on the face and then spreads to other parts of the body, most often the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
The rash, which can be extremely itchy, changes and passes through different stages and then subsides before eventually forming a crust. Lesions can cause scarring.
The infection usually clears up on its own and lasts between 14 and 21 days.
How is it noticed?
Monkeypox Virus can be spread when someone is in close contact with an infected person. The virus can enter the body through broken skin, respiratory tract or eyes, nose or mouth.
It was not previously identified as a sexually transmitted infection, but it can be transmitted through direct contact during sexual intercourse.
It can also be spread through contact with infected animals, such as monkeys, rats, and squirrels, or through infected objects such as bedding and clothing.
